I couldn’t face the same old Thanksgiving this year. Another tryptophan-laced orgy of food combined with marathon cleaning sessions before and after the big event, someone arriving with undisclosed food allergies, red wine on the carpet, cats eating the centerpiece and leftovers I have to look at with the dull eyes of the long married for weeks after the main event. No thank you!
So I did what any sane person would do: I went to Hawaii instead.
There, Thanksgiving was a Pina Colada-fueled homage to my ever present "SPF Burqa", sandy beaches and folks that unironically say “Brah.” I even tried surfing for the first time. And despite my deep-seated pleasure at a) not dying, b) not wiping out a la Greg Brady and the cursed tiki necklace, and c) standing up on at least one North Shore wave, I quickly learned after posting this picture that people did not necessarily share my enthusiasm or revel in my surfing accomplishments.
No, the most popular picture I posted was instead this gem, where a legion of people could see me wiping out like a boss.
I can’t claim to be particularly unique in this regard. In fact, it seems like the whole world likes nothing better than a deep dose of what the Germans would call schadenfreude, or “pleasure derived by someone from another person’s misfortune.” My full-on, Pacific Ocean-surfing-netti-pot photo was an exhibition of this lovely phenomenon writ small, reserved for those brave enough to call me “friend” on Facebook.
For a larger scale demonstration of schadenfreude, we had only to look as far as the hedge fund headlines in the last ten days or so. Some of my personal faves include:
“Hedge Funds Lick Wounds After Tough Year”
“Another Humbling Year For Hedge Funds”
“Hedge Funds Brace for Redemptions”
“Hedge Fund Giant Laments Profitability, Will Return $8 billion”
“Surprise! Hedge Funds Aren’t That Bad At Picking Stocks”
“The Incredible Shrinking Firms of Hedge Fund Billionaires”
Yeah, yeah, yeah…let’s all agree 2009 to present hasn’t been the easiest time to be a fan of alternative investments.
But let’s take a moment to put our keen delight in the misfortune of hedge funds into perspective.
Hedge funds aren’t exactly wiping out Greg Brady-style, either.
1) Yes, there have been closures & return of capital from some hedge funds, including a few large enough to be household names. BlueCrest opted to return outside investor capital, transitioning to a private investment partnership due to redemptions, fee pressure and its impact on recruiting. Avenue shuttered its hedge fund in favor of longer duration investments. Blackrock closed a macro fund that was down single digits for the year. Seminole returned $400 million of investor capital to better align the trading strategy with the markets and protect profitability, after returning 16% on average for the last 20 years. None of these are the spectacular, cry-during-an-MTV-performance, Justin Beiber-style meltdown, but rather strategic decisions we expect business owners to make daily.
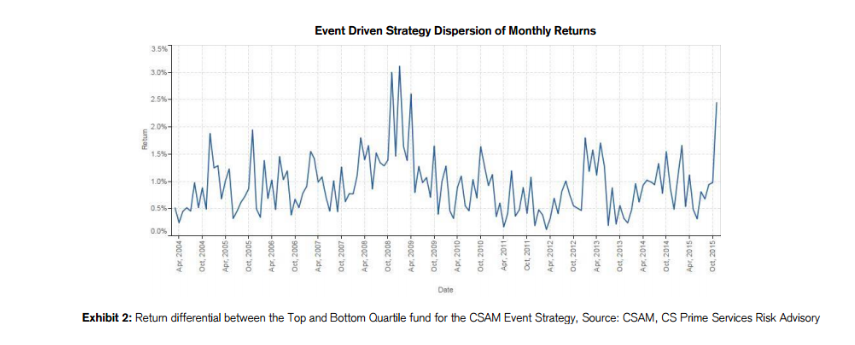
2) Yes, hedge funds haven’t exactly set the world on fire with 2015 performance. Or 2014 performance. Or 2013 performance…well, you get the picture. However, we have to remember, yet again, that the comparisons we’re making are average performance. If you look at return dispersion (here from Credit Suisse) even within single strategies of hedge funds, it is easier to remember that there are funds performing much better than the “average.”
(c) Credit Suisse Asset Management
3) Yes, hedge fund managers are losing money, but perhaps so are you. Given the explosion of institutional assets in hedge funds, celebrating the losses of a hedge fund could be tantamount to celebrating the losses of your favorite school teacher, fireman, police officer or other “main street” investor. And if that don’t take the wind out of your sails, I don’t know what will.
However, even with these clarifications, I am perhaps a little overdue in providing some hedge fund “tough love.” So here goes:
Hedge fund managers: Fee pressure is a pain. Expenses are up, regulation is increasing, the markets are more difficult to navigate and profitability is down. It’s unlikely that many of you will be able to weather a protracted double-digit or high single digit drawdown given the economic realities of managing a fund today and you’re less likely to be given the benefit of any doubt now than at perhaps any other time in hedge fund history.
But what protects fee structures and prevents increased regulation? Generating returns for your investors and doing the right things (disclosures, filings, investor relations, any and all regulatory filings) and doing it in a way that lets you sleep at night. This could be a watershed moment for hedged asset management. I wish I had a magic wand that would make it all easier but instead I can only say, for the love of all that’s holy, get ‘er done.